API Overview
A-Parser supports management via API, allowing the scraper to be integrated into complex systems (e.g., SaaS), leveraging A-Parser's capabilities from other programs and scripts.
The API is based on the HTTP protocol and JSON data serialization and can be used from any programming language
- curl
- NodeJS
- Perl
- Python
- PHP
curl http://127.0.0.1:9091/API \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"password":"123","action":"ping"}'
Result:
{"success":1,"data":"pong"}
const AParserClient = require('a-parser-client');
const AParser = new AParserClient('http://127.0.0.1:9091/API', '123');
AParser.ping()
.then(reply => console.log(reply.data))
.catch(err => console.log(err));
use AParser;
use Data::Dumper;
my $parser = AParser->new('http://127.0.0.1:9091/API', '123');
warn "Ping result:\n", Dumper $parser->ping();
from a_parser import AParser
aparser = AParser('http://127.0.0.1:9091/API', '123')
print(aparser.ping())
require_once 'aparser-api-php-client.php';
$aparser = new Aparser('http://127.0.0.1:9091/API', '123');
echo $aparser->ping();
Examples of use
- Calling and processing single or batch requests to any of the scrapers, for example:
- Getting a list of links from Google by query
- Translating text via Google Translate/Yandex Translator/DeepL
- Getting domain parameters, such as registration date, Alexa rank, and many others
- Queuing tasks and obtaining results
- Managing the task queue and controlling task status
- Automating the work of a scraper farm
Ready-made clients
Ready-made clients for A-Parser simplify working with the API:
NodeJS
Perl
PHP
Python
Request formation
Interaction with A-Parser occurs via the HTTP protocol with JSON serialization of the request and response. To make an API request, you need to execute a POST request to the address:
http://IP-сервера:9091/API
The following headers must be passed:
content-lengthcontent-type: application/json
The request body uses a JSON-serialized structure:
{
"password": "pass",
"action": "oneRequest",
"data": {
...
}
}
Where:
password- A-Parser passwordaction- the API method being calleddata- request parameters, unique to each request type; the full list and description are here
The general form of the response looks like this:
{
"success": 1,
"data": "..."
}
Where:
success- API request success, can be 1 or 0data- response to the called method, can be a scalar or an object, depending on the request type
Example code in PHP
We recommend using the client for PHP, this code without using a client is provided for informational purposes:
$aparser = 'http://127.0.0.1:9091/API';
$request = json_encode(array(
'action' => 'oneRequest',
'data' => array (
'parser' => 'SE::Google',
'preset' => 'Pages Count use Proxy',
'query' => 'test'
),
'password' => 'pass'
));
$ch = curl_init($aparser);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POST, 1);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, $request);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER, array('Content-Length: ' . strlen($request)));
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER, array('Content-Type: text/plain; charset=UTF-8'));
$response = curl_exec($ch);
curl_close($ch);
$response = json_decode($response, true);
echo $response['data']['resultString'];
Example code in Perl
We recommend using the client for Perl, this code without using a client is provided for informational purposes:
use LWP;
use JSON::XS;
my $aparser = 'http://127.0.0.1:9091/API';
my $request = encode_json {
'action' => 'oneRequest',
'data' => {
'parser' => 'SE::Google',
'preset' => 'Pages Count use Proxy',
'query' => 'test'
},
'password' => 'pass'
};
my $ua = LWP::UserAgent->new();
my $response = $ua->post(
$aparser,
'Content-Type' => 'text/plain; charset=UTF-8',
'Content-Length' => length $request,
'Content' => $request
);
if($response->is_success) {
my $json = decode_json $response->content();
print $json->{'data'}->{'resultString'};
}
else {
warn 'Response fail: ', $response->status_line();
};
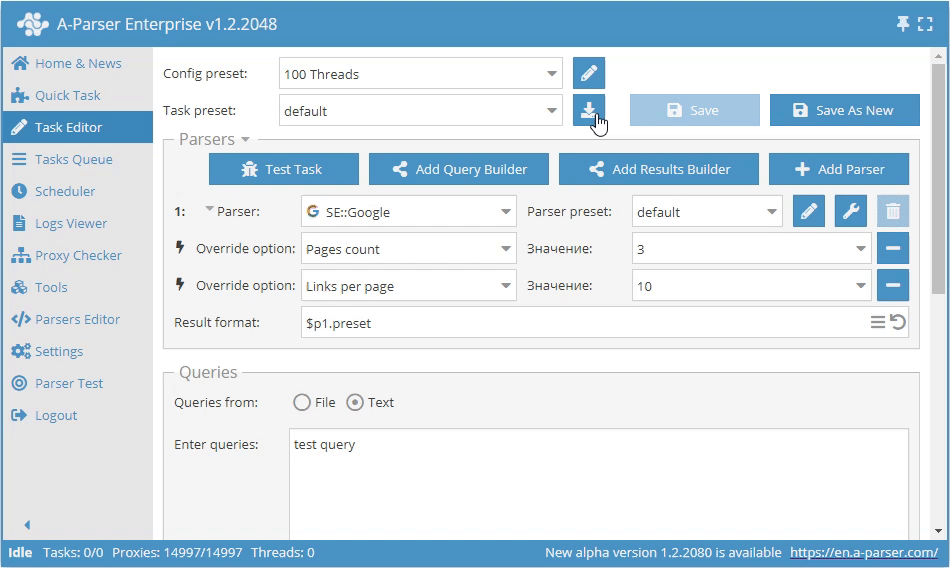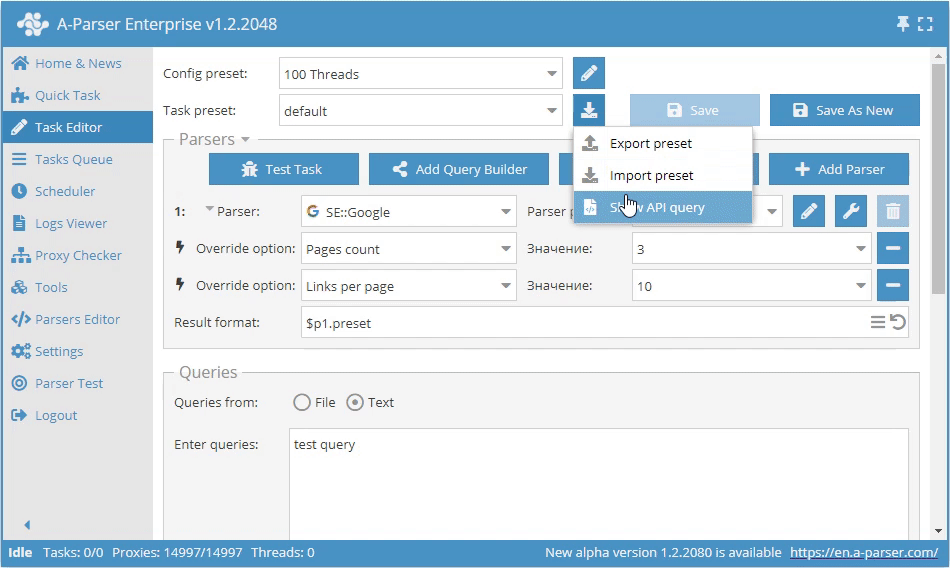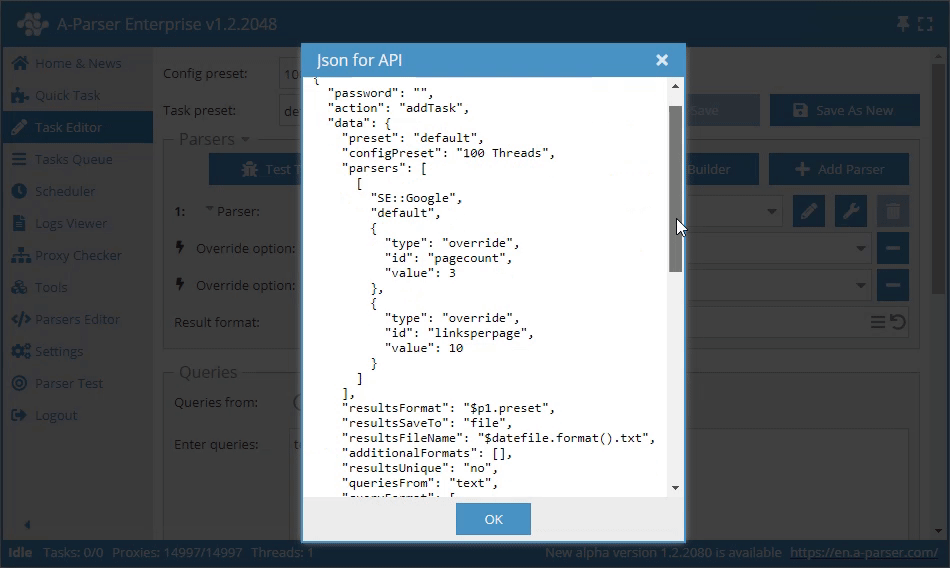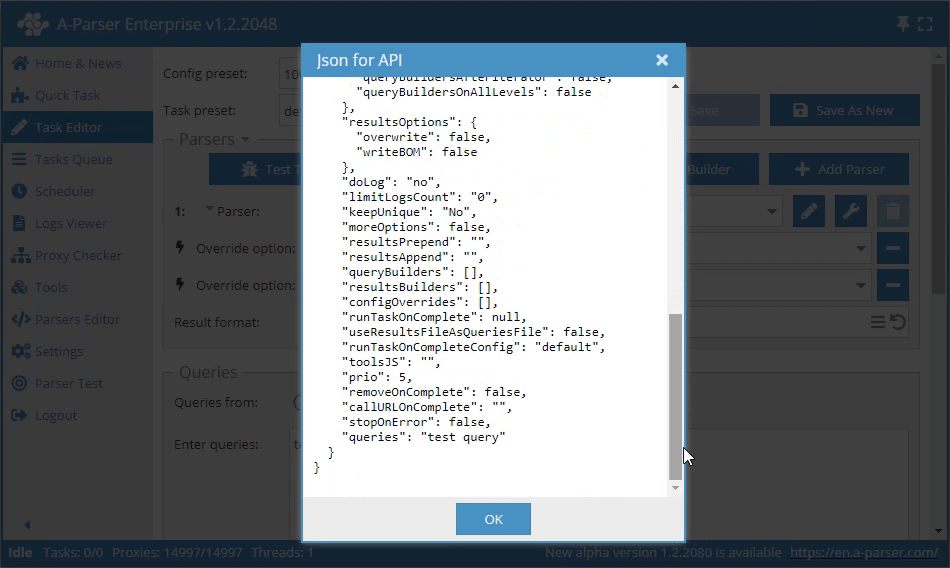
Getting the API request in the interface
The Get API Request function is available in the Task Editor to obtain the full API request. It allows you to get the complete JSON for use in the addTask method.
Redis API
Redis API is an alternative way to integrate A-Parser through a Redis server, providing greater flexibility and performance in some scenarios