Configuration via Interface
A-Parser allows you to set the configuration in a declarative style, as well as use the interface to create and edit presets without the need to modify the source code of the scrapers
static defaultConf
static defaultConf = {
version: '0.0.1',
results: {
flat: [
['title', 'Title'],
],
arrays: {
}
},
results_format: "Title: $title\n",
exampleKey: 'value',
};
The default scraper configuration; the config will be available in the class object via the property this.conf, The following fields are mandatory:
results- declaratively describes the results that this scraper can returnresults_format- sets the default result format
All other fields are optional; the following is a list of parameters that affect the scraper's operation:
| Parameter Name | Type | Description (default value) |
|---|---|---|
| timeout | number | Maximum request timeout in seconds (60) |
| useproxy | boolean / 0 / 1 | Defines whether to use a proxy (1) |
| max_size | number | Maximum size of the result file (1 * 1024 * 1024) |
| proxyretries | number | Number of attempts for each request; if the request fails to execute within the specified number of attempts, it is considered unsuccessful and skipped (10) |
| requestdelay | number / string | Delay between requests in seconds (0). A random value can also be set within a range, for example 10,30 - a delay from 10 to 30 seconds |
| proxybannedcleanup | number | Proxy ban time in seconds (600) |
| pagecount | number | Number of parsing pages (1) |
| parsecodes | { [code: string]: any } | Value of response codes for requests that will be considered successful (any) |
| queryformat | string | Request format ($query) |
| Parameter Name | Type | Description (default value) |
static editableConf
This setting specifies the list of configuration fields that can be edited via the interface. The following types of fields exist in the interface:
textfield- a field for arbitrary input of numerical and string valuescheckbox- a flag with on/off statescombobox- a dropdown for selecting one or multiple values- selection of multiple values is set via the option
{ multiSelect: 1 }
editableConf is an array, each element of which describes the corresponding configuration field:
static editableConf: [
...[
fieldName: string,
fieldConfig: [
fieldType: 'textfield' | 'combobox' | 'checkbox',
fieldLabel: string,
fieldOptions?: {},
...fieldValues: [fieldValue: any, valueTitle: string][]
]
][]
];
Example of declaring editable fields:
static get editableConf() {
let editableConf: typeof BaseParser.editableConf = [
['device',
['combobox', 'Device',
['desktop', 'Modern desktop computer (Windows 10, Chrome 84)'],
['mobile', 'Mobile device (iPhone X, iOS 11)']
]
],
['pagecount', ['combobox', 'Pages count']],
['linksperpage',
['combobox', 'Links per page',
[10, '10'],
[20, '20'],
[30, '30'],
[50, '50']
]
],
];
for (let page = 1; page <= 25; page++)
editableConf[1][1].push([page, page]);
return editableConf;
}
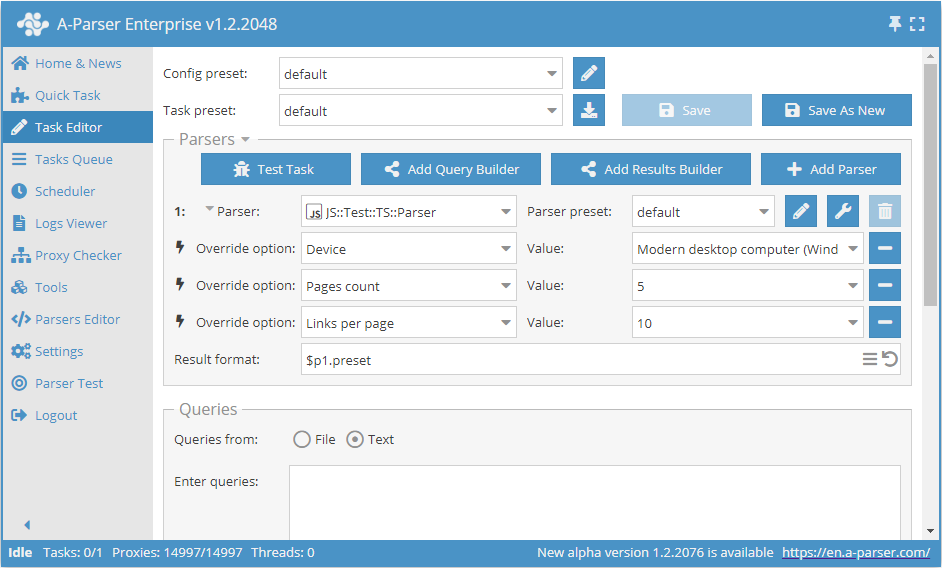
Note that in this example, a getter method is used for editableConf, which allows for additional processing, such as generating a list of pages. For simpler cases, you can set a static class property, similar to defaultConf
static parserOptions
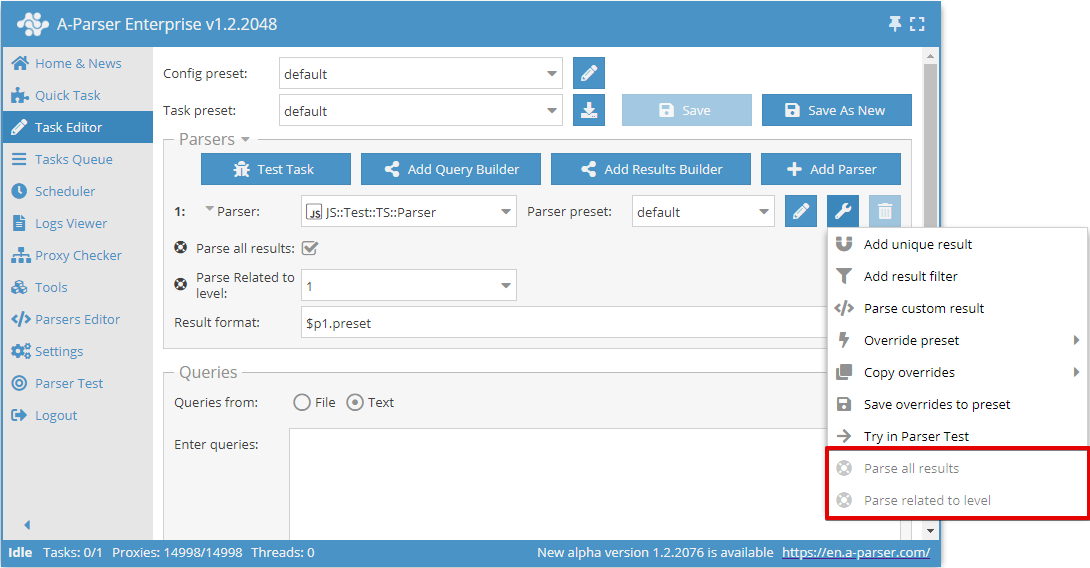
parserOptions is an alternative way to set settings; the list of options is displayed as additional items in the scraper's context menu
Option declaration works similarly to editableConf:
static parserOptions: [
...[
fieldName: string,
menuTitle: string,
fieldConfig: [
fieldType: 'textfield' | 'combobox' | 'checkbox',
fieldLabel: string,
fieldOptions?: {},
...fieldValues: [fieldValue: any, valueTitle: string][]
]
][]
];
Example of declaring additional fields:
static parserOptions: typeof BaseParser.parserOptions = [
['parseAll', 'Parse all results',
['checkbox', 'Parse all results']
],
['parseLevel', 'Parse related to level',
['combobox', 'Parse Related to level', [1, 1], [2, 2], [3, 3]]
],
];