Result Uniqueness
Uniqueness, deduplication, removal of duplicates, and removal of repetitions all mean that we do not need repeating results. In A-Parser there are 2 methods of making results unique; let's examine each one in detail.
Uniqueness of results by string
This method works after result formation, immediately before writing the result to the file, each line is checked for uniqueness, and only new unique lines are written to the file.
See also: Order of request processing
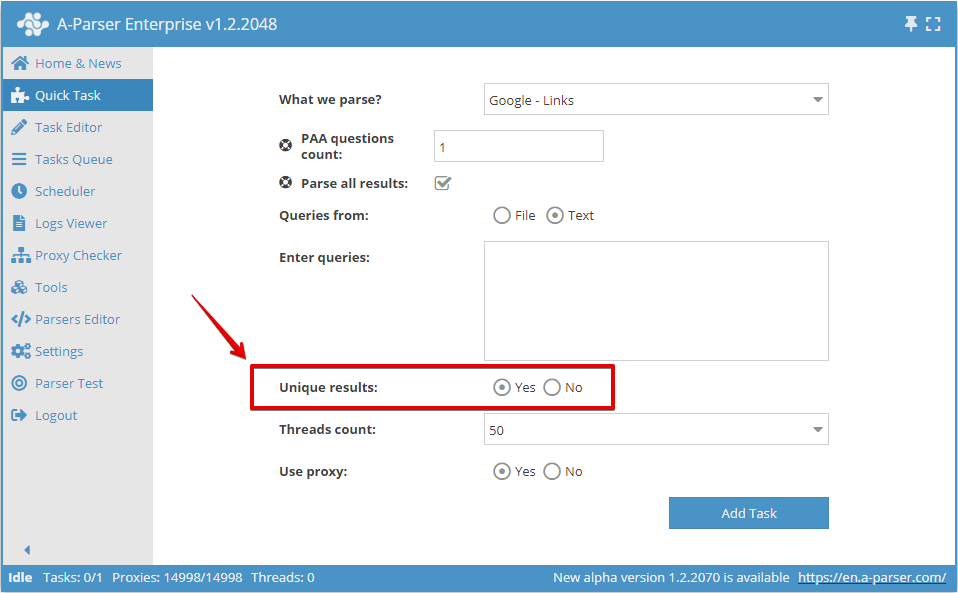
String-based uniqueness can be enabled in a Quick Task:
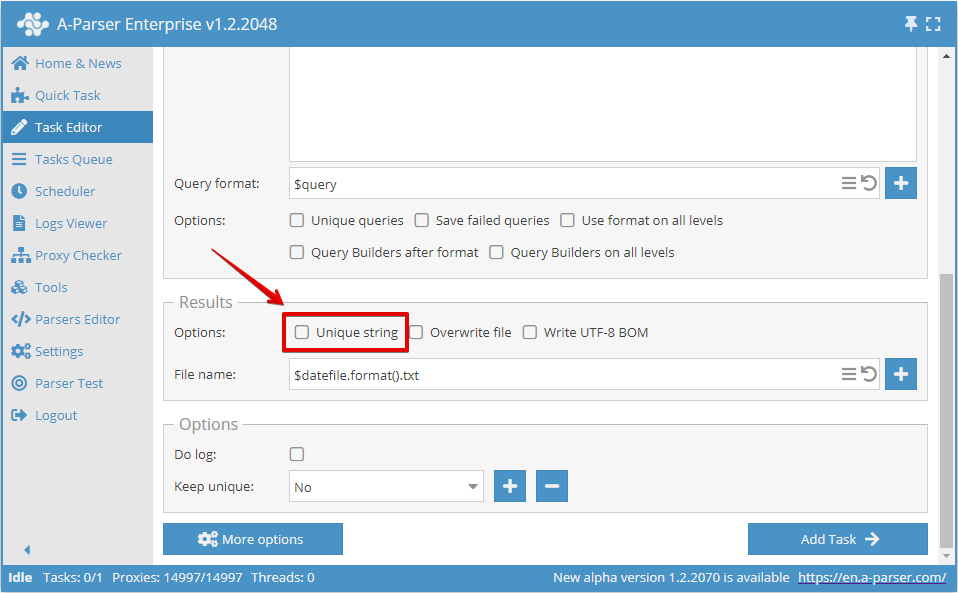
Or in the Task Editor:
Uniqueness by any result
Uniqueness by any result allows you to apply uniqueness directly to the selected result from a specific scraper. You can add this type of uniqueness in the Task Editor by clicking on the tool icon to the right of the scraper and pressing Add uniqueness:
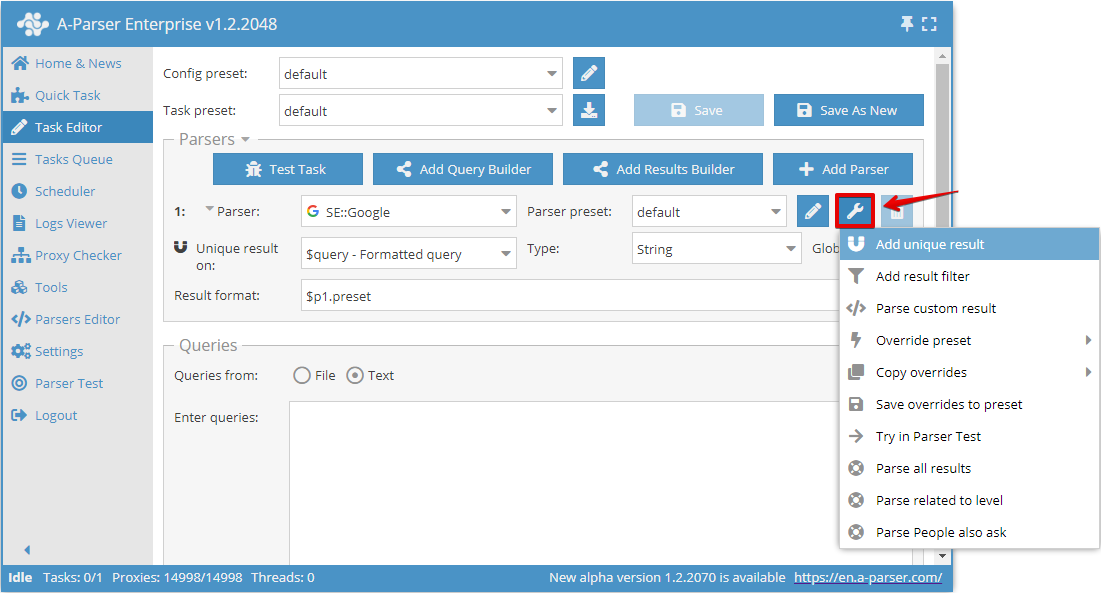
Now you can select which result to apply uniqueness to and the type of uniqueness:
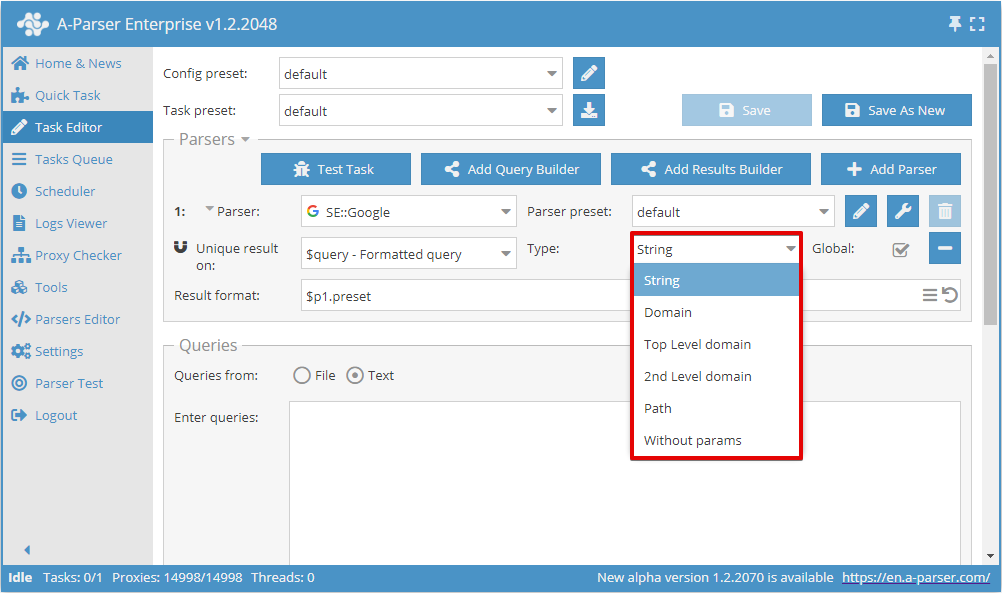
The Global switch is used when 2 or more scrapers are selected; it determines whether to perform general uniqueness or unique results for each scraper separately.
Uniqueness types
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| String | Uniqueness by string (compares the entire result string) |
| Domain | Uniqueness by domain (compares the entire domain, e.g., www.domain.com and domain.com are different domains) |
| Top-level domain | Uniqueness by main domain, considering regional, commercial, educational, and other domains (e.g., domain.co.uk and domain2.co.uk are different domains, but sub1.domain.com and sub2.domain.com are the same) |
| Second-level domain | Uniqueness by second-level domain (compares second-level domains, e.g., www.domain.com, domain.com, and user.subdomain.domain.com are all the same domain) |
| Path | Uniqueness by path (compares parts of the link up to the file, e.g., http://domain.com/path1/file.php and http://domain.com/path1/file2.php have the same path parts up to the file) |
| Without parameters | Uniqueness by link without parameters (compares links ignoring parameters, e.g., http://domain.com/file.php?page=1 and http://domain.com/file.php?page=2 are the same links) |
Query uniqueness
Query uniqueness sends only unique queries, that have not been scraped previously in the current task, directly to scraping. Main use cases:
- If there are duplicates in the initial queries and you don't want to scrape them (double work)
- When using the Scrape up to level option, it is necessary to use only unique queries to prevent queries from expanding and looping (for example, when using the
 HTML::LinkExtractor)
HTML::LinkExtractor)
In all other cases, unnecessary use of query uniqueness will only slow down the overall operation of the scraper
Keeping uniqueness across tasks
It is possible to save the uniqueness database for use in future tasks, which allows you to save only new unique results in new tasks (for example, links when scraping SERPs in  SE::Google)
SE::Google)
To save the uniqueness database, you need to create a new database name when adding the first task:
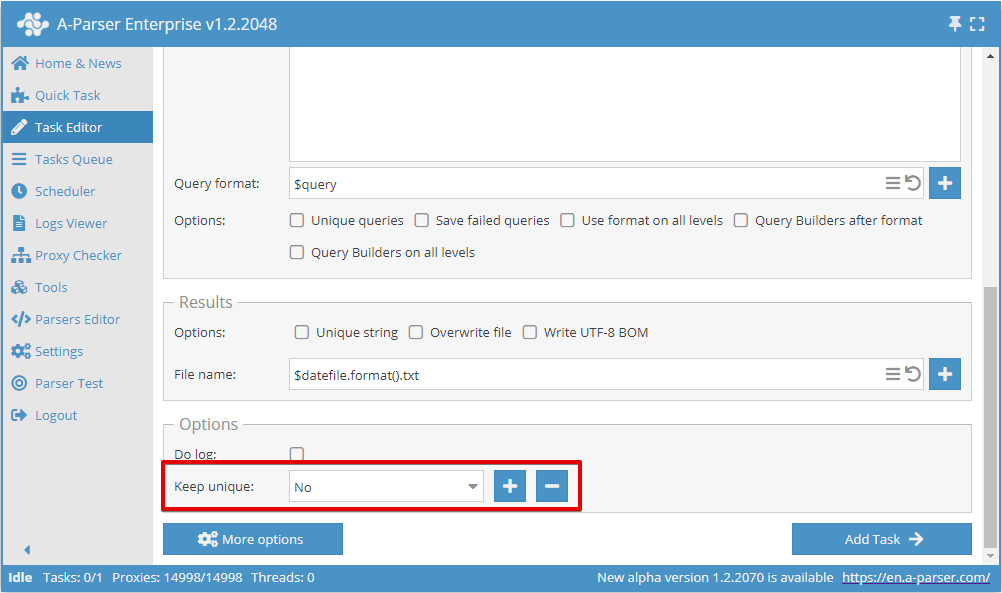
For all subsequent tasks, you must select the previously created database name, which will save only new unique results, regardless of whether the results are written to the same file as in the first task or to a new file.