Using Regular Expressions
General Information
Perl/JavaScript-compatible regular expressions are used in A-Parser , which can be used:
- When scraping arbitrary information from any site
- In the Query Builder for extracting or replacing a part of the query
- In the Results Builder for transforming any results
- When using filters
- In the Regular Expression Constructor
- When checking the availability of the next page in the A-Parser
 Net::HTTP
Net::HTTP
Detailed documentation on regular expressions can be found in the following sources:
- Regular Expressions on WikiPedia
- Universal encyclopedia of PCRE standard regular expressions
- Topic Sharing RegExes on the forum
In A-Parser it is possible to process any result using a regular expression, for this the option Use RegEx:
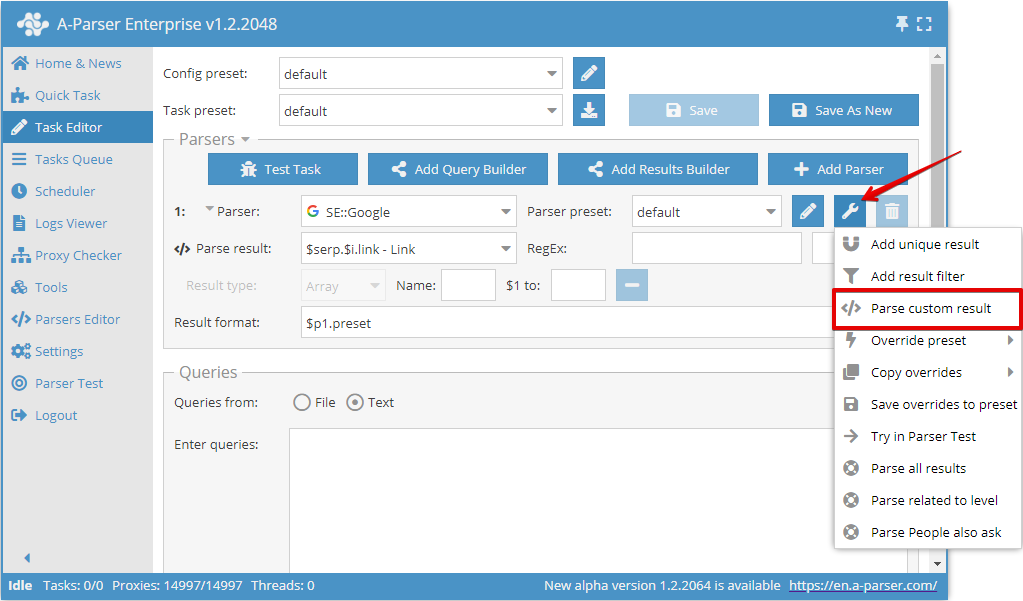
Usage Specifics and Flags
- Regular expressions are written without delimiters
// - The following flags are supported:
- i - case-insensitive search
- g - global search or replacement
Extraction of Arbitrary Information
- In Result Type, the result type is specified:
Flat(simple result) orArray(array). If an array is selected as the source result or the g flag of the regular expression is used, the result will always be saved in an array. The array name is specified in the Name field.
(?m)^(.+?test.+?)$
Extracting Arbitrary Information
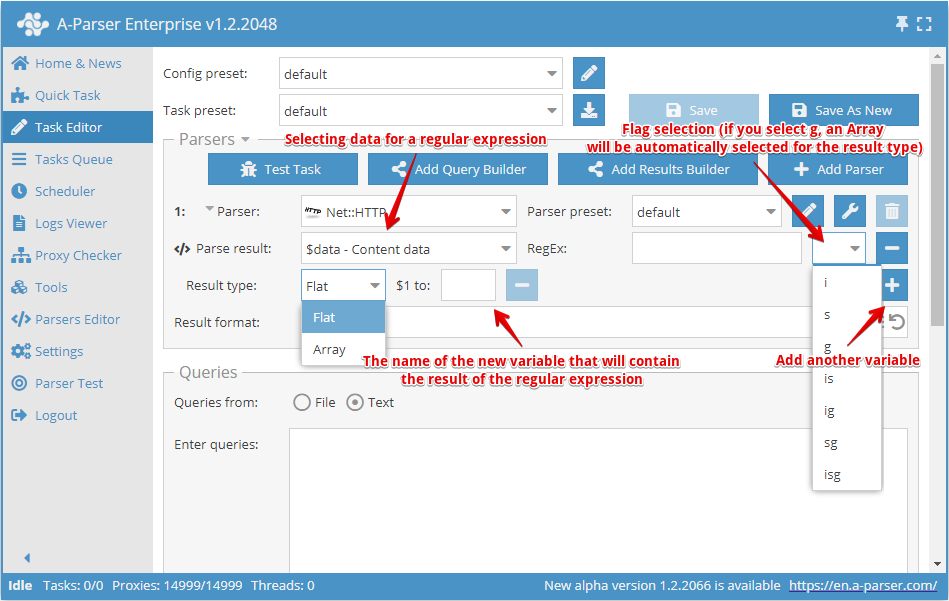
Using the option Use RegEx or the Results Constructor it is possible to use regular expressions to extract arbitrary information from scraping results, for example from the source HTML code of pages or from already prepared results
- As Apply to , the result from the scraper is selected, which can be a simple result or an array
- The regular expression is specified without delimiters, followed by the option to specify a flag
- Result Type specifies the result type:
Flat(simple result) orArray(array). If an array is selected as the source result or the g flag of the regular expression is used, the result will always be saved as an array. The Name field specifies the array name. - Each capturing group of the regular expression can be saved as a separate element; the element name is written in the corresponding field $1 to, $2 to... - where the digit denotes the number of the capturing group
- In the RegEx field you can use the templater, which allows using the query as part of the regular expression
The newly created results can be used for result formatting, in the Results Constructor, , in filtering and deduplication of results or in the next Use RegEx.
This option is similar to the results builder when using RegEx Match
Example of scraping image links from source HTML code
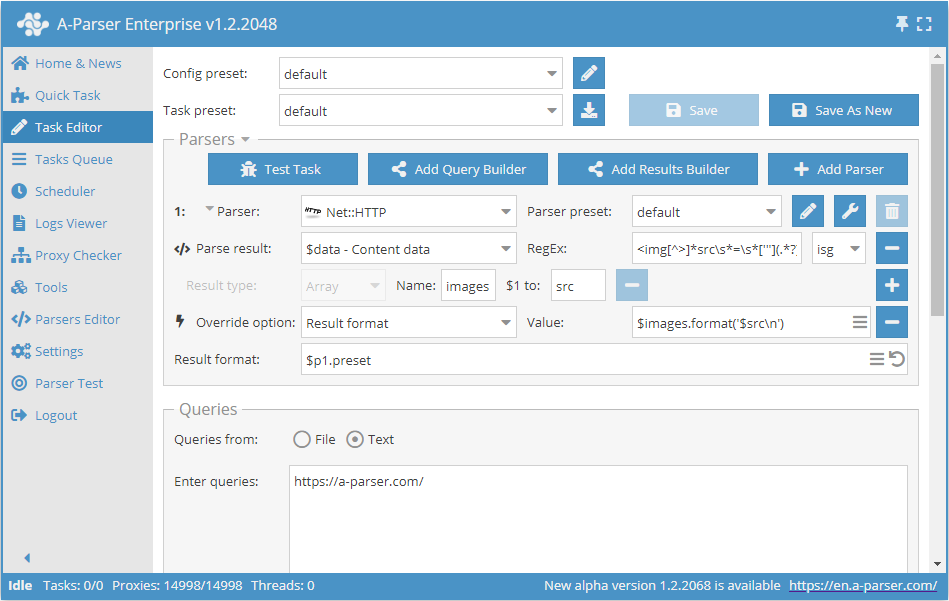
To solve this problem, we use the  Net::HTTP scraper to get the source code of the page.
We apply to
Net::HTTP scraper to get the source code of the page.
We apply to $data (#) a regular expression with flags isg, , and save the result to the elements src of the array images.
In the result format, we specify that all src elements should be output separated by a newline.
As a result of the scraping for the query http://a-parser.com/, we will get the following list in the result file:
/img/lang/en.png
/img/lang/ru.png
img/[email protected]
https://files.a-parser.com/img/site/tour_ru/V1qpV.png
https://files.a-parser.com/img/site/tour_ru/tour_ru_1_all_parsers_list.png
https://files.a-parser.com/img/site/tour_ru/tour_ru_1_quick_task.png
https://files.a-parser.com/img/site/tour_ru/tour_ru_2_task_editor_easy.png
https://files.a-parser.com/img/site/tour_ru/tour_ru_3_task_editor_analyze_domains.png
https://files.a-parser.com/img/site/tour_ru/tour_ru_4_task_editor_parse_emails.png
https://files.a-parser.com/img/site/tour_ru/tour_ru_5_queue_fast_google.png
https://files.a-parser.com/img/site/tour_ru/tour_ru_6_queue_spyserp.png
https://files.a-parser.com/img/site/tour_ru/tour_ru_7_javascript_parser.png
https://files.a-parser.com/img/site/tour_ru/tour_ru_8_scheduler.png
https://files.a-parser.com/img/site/tour_ru/tour_ru_9_settings.png
https://files.a-parser.com/img/site/tour_ru/tour_ru_10_proxies.png
https://files.a-parser.com/img/site/tour_ru/tour_ru_11_templates.png
https://files.a-parser.com/img/site/tour_ru/tour_ru_12_task_tester.png
https://files.a-parser.com/img/site/tour_ru/tour_ru_13_parser_test.png
https://files.a-parser.com/img/site/tour_ru/tour_ru_14_api.png
https://files.a-parser.com/img/site/tour_ru/tour_ru_15_resources.png
data/avatars/s/0/12.jpg?1507557563
data/avatars/s/0/12.jpg?1507557563
data/avatars/s/13/13392.jpg?1570706020
data/avatars/s/16/16560.jpg?1586782475
data/avatars/s/1/1240.jpg?1537376153
styles/uix/xenforo/avatars/avatar_s.png
data/avatars/s/0/371.jpg?1412969226
styles/uix/xenforo/avatars/avatar_s.png
//mc.yandex.ru/watch/26891250
Download example
How to import the example into A-Parser
eJxtVN9v2jAQ/l8sJArqYH3YS7Stokhomxgwmj5BJlnkyLz612yHFUX533d2Egfa
vYDv7rvvvvNdXBFH7bPdGLDgLEl2FdHhTBKSw5GW3JFboqmxYHx4R1bgkuRLmm7Q
HxEVcWcNmHMorVNiC7ZJNM0BuaijwS7gBc2PTBS7n5+zsTWH/d6OP/mf3XBPspvJ
+H4UTh08bZiZLSJh66LG0DM6w/+KigATtAAbkV4zwSIkq3uR6gTGsBwQxXK0j8oI
6kwn+kR56WGDhmvShG+GgyBWDkekzrJYYBGiHq7vJu3dxeAjPUGqfAnGoXcv0Gr1
DvBmwEe7MqOJe/EMNM+ZY0pS3lTwnfRVnyT7E0RKhVg8GgZ2YZRAl4NA4J3nTt2O
DIJNkKIMuT+aHJIcKbdwSyxKXVAUkr+OMAeGOmXW2utBf0WUnHG+hBPwHhb4H0rG
c1yV2RGTvraJ/4es33DUsb3LUjisvwY1RJZgPay/91m5WqqiuwzOBHNo27kqpR/M
e3Q+A+h4ZysPE8pALNMyt9Xxa9Ag/Wb0I5vp3nXVxtVYrp0HJY+sWLfb1iFLmeIn
t5ZzJTQH35csOcexWNj26zGz7Ri80Qt8nTwPJa4+VqcUt98eG6naMFy/D16gwJu8
rNpSHijnT9vlZYT0K4XGL+e0TaZT+q55BiYHJabEJzooFK4UtlVn8ZGIT0l18VQk
VY1j+m03Dcb35BHow8uxOAOS3NX/AFJvlP8=
Regular Expression Constructor
The Regular Expression Constructor was added starting from version 1.2.78.
You can find it on the Tools tab -> Regular Expression Constructor. You can also send the received page code directly in Test Scraping. To do this, you need to enable debug mode and click on the Go to RegEx Builder link.
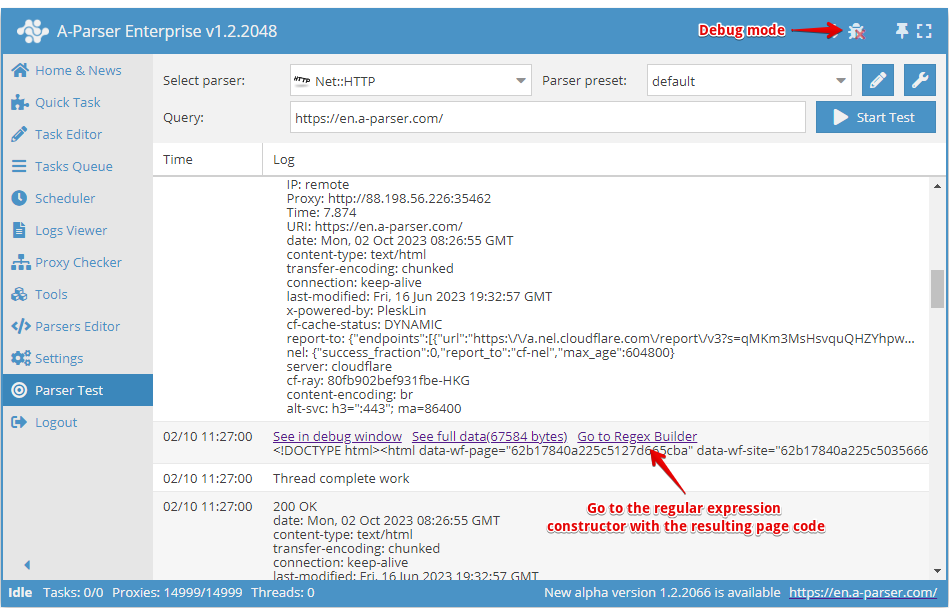
The constructor allows you to select the programming language in which the resulting regular expressions will be used.
To work with the constructor, you need to insert the source text into the left field (or it will be inserted automatically from Test Scraping when transitioning via Go to Regex Builder). On the right, you configure the parameters of the future regular expression.
To create a simple Regular Expression (for example, to get the title) it is enough to specify the necessary elements of the regular expression.
- In the Before Group field, enter the characters that precede the information we need
- In the After Group field, enter the characters that follow the required data
- In the Group Starts With field, specify the characters with which the desired string should begin
- In the Group Ends With field, specify the characters that should be at the end of the desired string
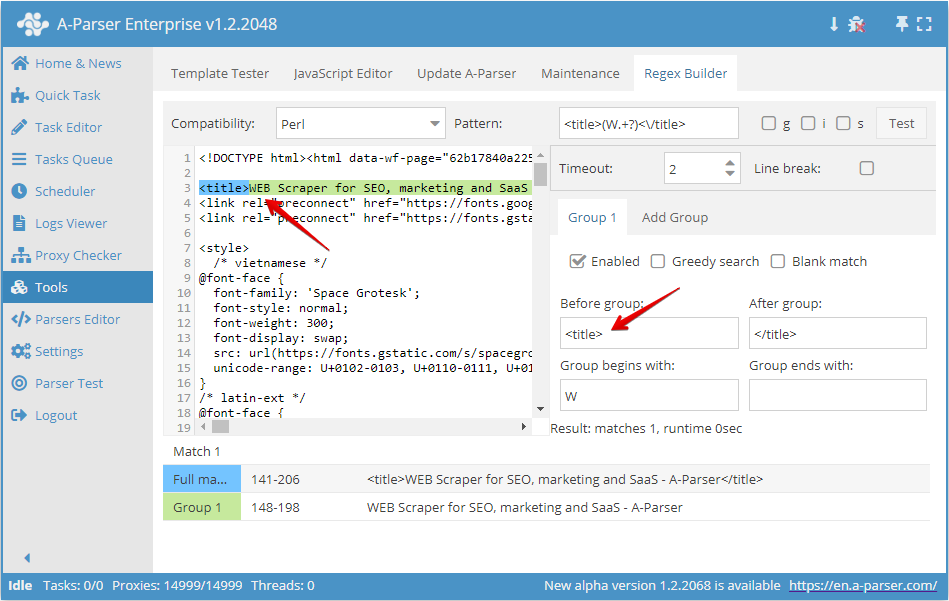
As seen in the screenshot above, we create a regular expression that will select the site's title. Before the group we put <title> and after the group </title>, , and also, for example, indicate that the desired string starts with the letter W.
For full testing of the resulting regular expression, it is possible to enable the necessary flags: g, s and i.
It is also possible to create more complex regular expressions with 2 or more groups.
For example, let's try to create a regular expression to collect all links and anchors in the list <li>. For this, we need to enable the flag g and add another search group, as the first group will contain links, and the second will contain anchors.
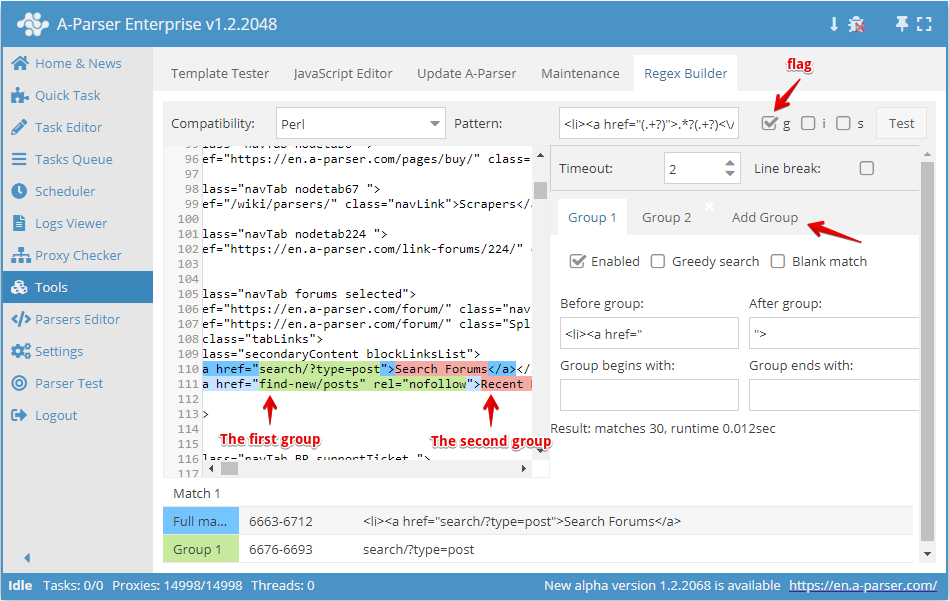
By setting the necessary parameters for both groups, we get the regular expression:
<li><a href="(.+?)">(.+?)<\/a
To test the regular expression, click the Test button:
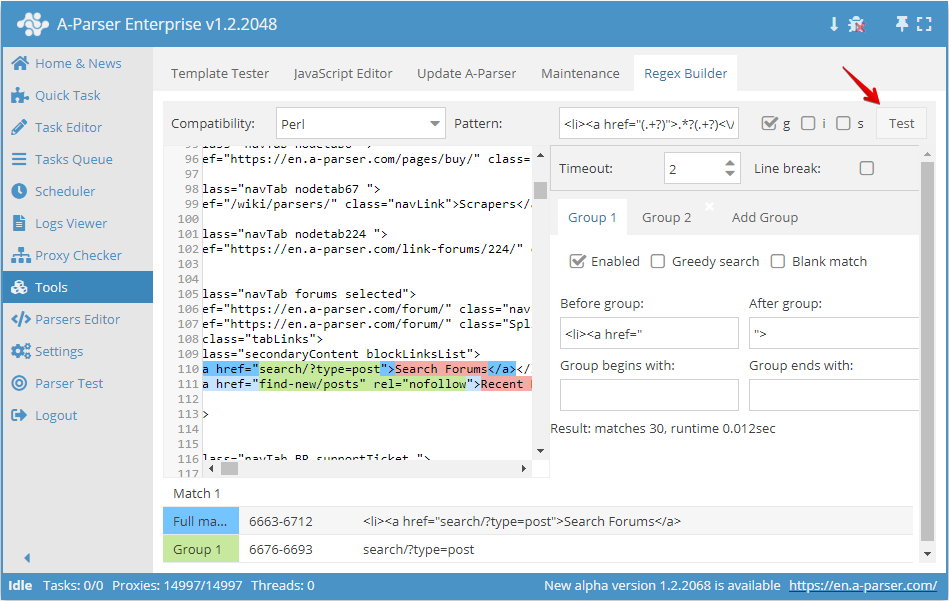
After the regular expression is executed, the result of its work is displayed at the bottom: the full string and the captured groups. Double-clicking on any element in the result table scrolls the initial text to the location of that match.
Useful Links
🔗 RegEx for the very small
My name is Vitaly Kotov and I know a little bit about regular expressions. Below the cut, I will explain the basics of working with them...
🔗 RegEx (regexp) — basics
Regular expressions — are a mechanism for finding and replacing text. In a string, a file, multiple files...
🔗 ⏩Scraping a catalog of industrial equipment
An example of using regular expressions when scraping a catalog of industrial equipment
🔗 ⏩Scraping the Booking.com resource
An example of using regular expressions when scraping the Booking.com resource
🔗 ⏩Finding contact pages
An example of using regular expressions when scraping contact pages