Query Formatting
Query format - allows you to add substitutions and format the query to the desired view using templates; it is applied to each query.
Query Formats
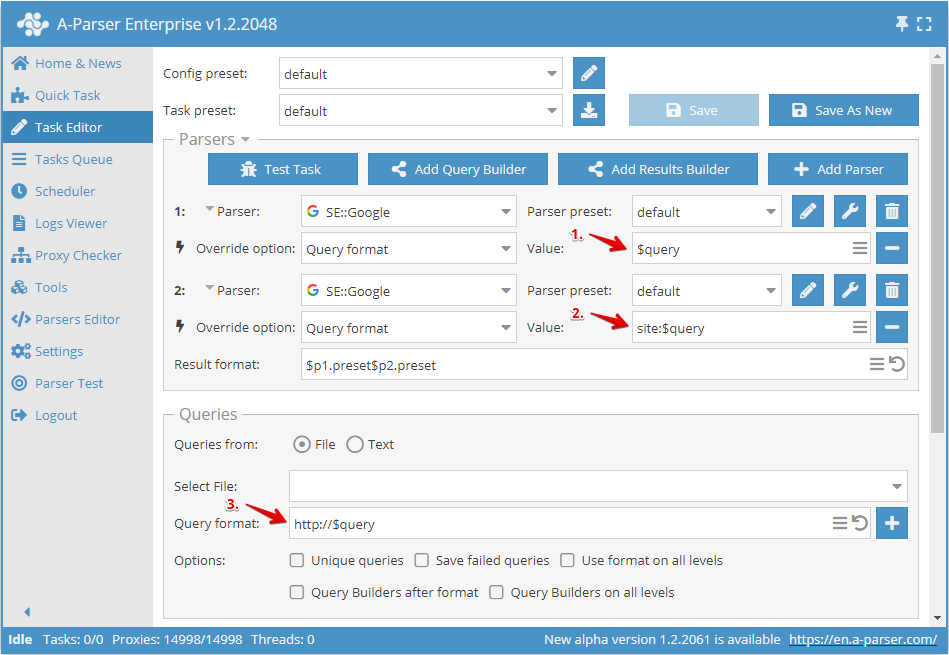
- Query format for the 1st scraper
- Query format for the 2nd scraper
- General query format
There are 2 ways to specify the template:
- General query format, it is processed first and supports substitutions
- Query format for each scraper - allows setting a specific format for individual parsers
Let's analyze the example in the screenshot, assuming that we use a file with a list of domains as queries, like this:
google.com
a-parser.com
yandex.ru
The general query format is specified as:
http://$query
The string http://, will be prepended to each original query (domain), and the query will be converted google.com -> http://google.com
The query format for the 1st scraper remained unchanged, it will parse the query http://google.com
The query format for the 2nd scraper looks like this:
site:$query
The query for this scraper will be converted: http://google.com -> site:http://google.com
Query Templates
The query format fully supports the templating engine Template Toolkit, with the following available variables:
$query- the query after formatting using the general result format$query.num- the sequence number of the query$query.lvl- the nesting level of the query when using the options Parse to level or Parse all results$query.orig- the original query before formatting$query.first- the first query when using the options Parse to level or Parse all results$query.prev- shows the query that was at the previous level, works for HTML::LinkExtractor, $tools.query.add and JS scrapers this.query.add
HTML::LinkExtractor, $tools.query.add and JS scrapers this.query.add- All variables created via Query constructor
Substitution Macros
The General Query Format supports the following macros:
| Macro | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| {az:START:END} | Substitution of a digital-symbol sequence. Instead of START, the beginning of the sequence is specified, and instead of END, the end. The length of END must be greater than or equal to the length of START. The symbols at the end of the END sequence must be after (in alphabetical order) the symbols at the beginning of the START sequence. Any UTF-8 character sequences can be used | {az:a:z} - substitution of all symbols from a to z (a, b, c, ..., x, z). {az:aaa:zzz} - substitution of all symbols from aaa to zzz (aaa, aab, aac, ..., zzx, zzz). {az:a:zz} - substitution of all symbols from a to zz (a, b, c, ... aa, ab, ..., zx, zz). {az:00:99} - substitution of all numbers from 00 to 99 (00, 01, 02, ..., 98, 99). {az:а:яяя} - substitution of all Cyrillic symbols from а to яяя (а, б, ... аа, аб, ... яяю, яяя) |
| {each:WORD1,WORD2,...} | Substitution of the specified words WORD1, WORD2, etc., unlimited length | {each:green,blue,red,black} - substitution of the words green, blue, red, black. {each:,buy,sell} - substitution of an empty word, then buy and sell |
| {subs:NAME} | Substitution of additional words from files in the queries/subs/ folder. Instead of NAME, you must specify the file name, without the .txt extension | {subs:zones} - substitution of all lines from the file queries/subs/zones.txt |
| {num:START:END} | The macro iterates through numbers in the specified range. Instead of START, the beginning of the interval is specified, and instead of END, the end. Fractional numbers are supported. | {num:1:1000} - substitution of all numbers from 1 to 1000 (1, 2, 3 ..., 999, 1000) |
| {num:START:END:STEP} | The macro iterates through numbers in the specified range, with the specified step. Instead of START, the beginning of the interval is specified, instead of END, the end, and instead of STEP, the step. Fractional numbers are supported. | {num:0:1000:10} - substitution of all numbers from 0 to 1000 with a step of 10 (0, 10, 20 ..., 990, 1000) |
| {num:END:START} | The macro iterates through numbers in the specified range in reverse order. Instead of END, the end of the interval is specified, START specifies the beginning of the interval. Fractional numbers are supported. | {num:1000:1} - substitution of all numbers from 1000 to 1 (1000,999, 998, ..., 2, 1) |
| {num:END:START:STEP} | The macro iterates through numbers in the specified range in reverse order, with the specified step. Instead of END, the end of the interval is specified, START specifies the beginning of the interval, and instead of STEP, the step. Fractional numbers are supported. | {num:1000:1:10} - substitution of all numbers from 1000 to 1 with a step of 10 (1000,990, 980, ..., 10, 1) |
⏩ Video: Substitution Macros
This video covers:
- macro
{num}on examples of iterating through pages and coordinates in the scraper Maps::Google
Maps::Google - the
{az}macro on the example of parsing with inurl: to increase the number of queries and, consequently, results - the
{each}macro on the example of parsing suggestions to generate phrases
Combining Substitution Macros
Substitution macros can be combined. Complex example:
$query site:{subs:zones} {az:aa:zz}
Suppose one of the queries for scraping was viagra, and the file queries/subs/zones.txt contains the following list of zones: com, net, org, then the following set of combinations will be sent for scraping:
viagra site:com ab
...
viagra site:net jj
...
viagra site:eek.rg zz
The total number of queries will correspond to the multiplication of possible combinations:
1 query (viagra) x 3 zones ({subs:zones}) x 676 character variations ({az:aa:zz}) = 2028 queries