SE::Yandex::WordStat::ByDate - Scraper of Yandex WordStat impression statistics by month or week
Overview of the scraper
Wordstat - is a Yandex service designed to evaluate user interest in various topics and select keywords for SEO optimization and contextual advertising. Additionally, Yandex Wordstat can be used to assess the seasonality and geographic dependence of search queries.
The Yandex WordStat by date scraper supports automatic query expansion, ensuring you get the maximum number of results from the SERP. A-Parser can also automatically follow related queries up to a specified depth.
A-Parser's functionality allows you to save scraping settings for future use (presets), set a scraping schedule, and much more. You can use automatic query expansion, substitution of sub-queries from files, iteration over alphanumeric combinations and lists to get the maximum possible number of results.
Results can be saved in the form and structure you need, thanks to the built-in powerful templater Template Toolkit which allows applying additional logic to the results and outputting data in various formats, including JSON, SQL and CSV.
Scraper use cases
🔗 Wordstat bydate automation
Used to store up-to-date information in the database, and generates a fresh CSV with each run
Accounts
The Yandex accounts are required for the  SE::Yandex::WordStat::ByDate scraper to work. Accounts can be registered using the
SE::Yandex::WordStat::ByDate scraper to work. Accounts can be registered using the  SE::Yandex::Register scraper or simply add existing accounts to the
SE::Yandex::Register scraper or simply add existing accounts to the files/SE-Yandex/accounts.txt file in a supported format.
Alternatively, you can enable account registration "on the fly".
Collected data
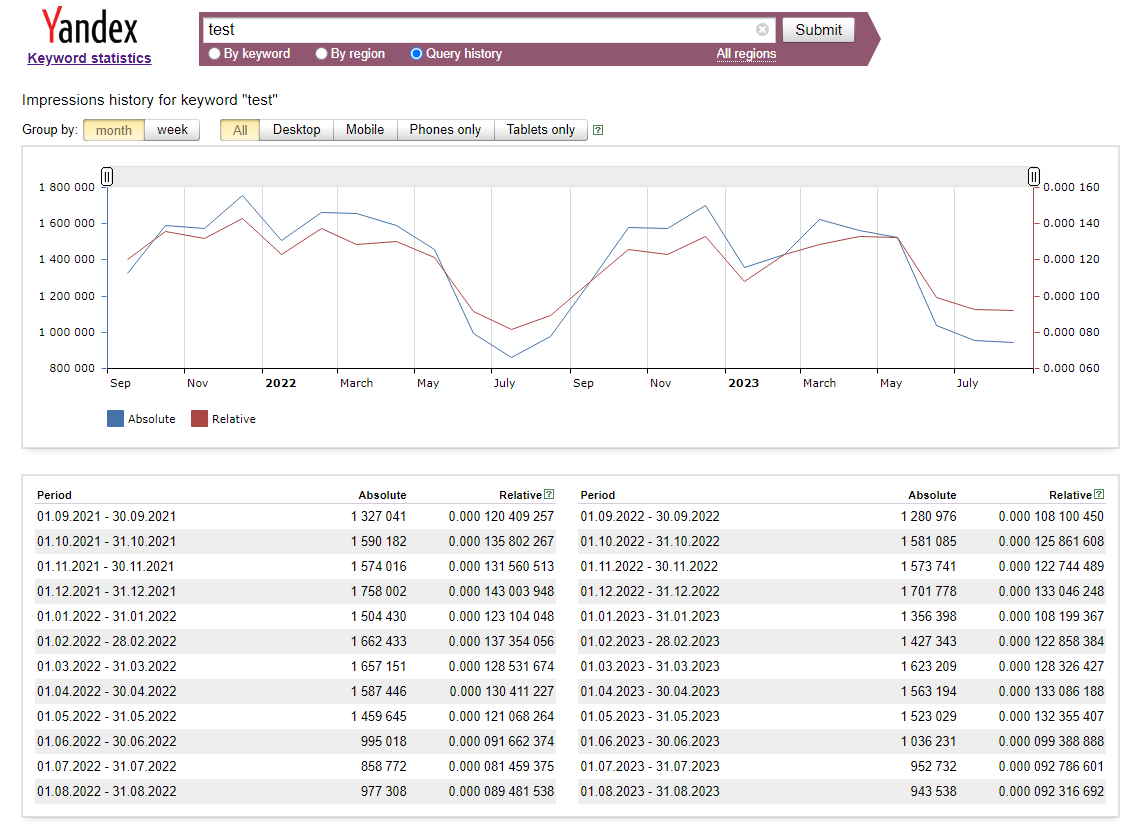
- Keyword statistics by month or week
- Date
- Absolute value
- Relative value
Capabilities
- Supports selection of search region (with subgroups)
- Ability to select multiple regions for evaluation
- Support for automatic bypass of Smart Captcha and the ability to bypass graphical captcha using the AntiCaptcha service or any other service that supports their API
- Device type selection
- Ability to choose the authorization method
- Ability to register accounts "on the fly"
- Supports working with the extended account format and can answer a secret question (if the answer is in
info). It also uses the saved proxy for authorization (if present ininfo).
Use cases
- Assessing traffic volume by keyword
- Identifying seasonal keywords
Queries
For queries, you should specify keywords, just as you would enter them directly into the Wordstat search form, for example:
test
Output result options
A-Parser supports flexible result formatting thanks to the built-in templater Template Toolkit, which allows it to output results in an arbitrary form, as well as in a structured format, such as CSV or JSON
Default output
Result format:
Views:\n$views.format('$date $count $relcount\n')
The result displays keyword statistics for the month and week:
Monthly:
2011-09-30 3010832 0.0008903808
2011-10-31 681432 0.0001825883
2011-11-30 628532 0.0001575008
2011-12-31 629072 0.0001495699
2012-01-31 561206 0.0001300651
2012-02-29 572039 0.0001290000
2012-03-31 614897 0.0001225754
2012-04-30 520433 0.0001185340
2012-05-31 521967 0.0001235327
2012-06-30 502568 0.0001299958
...
Weekly:
2012-09-16 118715 0.0001222877
2012-09-23 120799 0.0001211773
2012-09-30 137809 0.0001365837
2012-10-07 133929 0.0001313643
2012-10-14 140373 0.0001293922
2012-10-21 136014 0.0001242209
2012-10-28 148350 0.0001293328
2012-11-04 139556 0.0001232566
2012-11-11 154830 0.0001314057
2012-11-18 136458 0.0001147489
2012-11-25 149463 0.0001261401
2012-12-02 144724 0.0001197564
2012-12-09 149142 0.0001212195
2012-12-16 162864 0.0001298181
Output to CSV table
Result format:
[% FOREACH i IN views;
tools.CSVline(query, i.count, i.date);
END %]
Example result:
"test",9661734,2012-03-31
"test",8567243,2012-04-30
"test",9028986,2012-05-31
"test",6082099,2012-06-30
"test",5531950,2012-07-31
"test",5214663,2012-08-31
"test",6603865,2012-09-30
"test",9127457,2012-10-31
"test",9238652,2012-11-30
Saving in SQL format
Result format:
[% FOREACH i IN views;
"INSERT INTO views VALUES('" _ query _ "', '"; i.count _ "', '"; i.relcount _ "', '"; i.date _ "')\n";
END %]
Example result:
INSERT INTO serp VALUES('test', '9661734', '0.0019259985', '2012-03-31')
INSERT INTO serp VALUES('test', '8567243', '0.0019512785', '2012-04-30')
INSERT INTO serp VALUES('test', '9028986', '0.0021368683', '2012-05-31')
INSERT INTO serp VALUES('test', '6082099', '0.0015732140', '2012-06-30')
INSERT INTO serp VALUES('test', '5531950', '0.0013160071', '2012-07-31')
INSERT INTO serp VALUES('test', '5214663', '0.0013327945', '2012-08-31')
INSERT INTO serp VALUES('test', '6603865', '0.0015936909', '2012-09-30')
INSERT INTO serp VALUES('test', '9127457', '0.0018740506', '2012-10-31')
INSERT INTO serp VALUES('test', '9238652', '0.0018308715', '2012-11-30')
Dump results to JSON
Общий формат результата:
[% IF notFirst;
",\n";
ELSE;
notFirst = 1;
END;
obj = {};
obj.views = [];
FOREACH item IN p1.views;
obj.views.push({
date = item.date
relcount = item.relcount
count = item.count
});
END;
obj.json %]
Начальный текст:
[
Конечный текст:
]
Example result:
[{
"views": [
{
"count": "9661734",
"date": "2012-03-31",
"relcount": "0.0019259985"
},
{
"count": "8567243",
"date": "2012-04-30",
"relcount": "0.0019512785"
},
{
"count": "9028986",
"date": "2012-05-31",
"relcount": "0.0021368683"
}
]
}]
See also: Result Filters
Available settings
| Parameter | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Period | Monthly | Selection of the period (Monthly/Weekly/Daily, Daily works only with Use Wordstat 2 option enabled) |
| Start date | | Specifies the start date for search. Works only with Use Wordstat 2 option enabled. Must take into account date specification rules |
| End date | | Specifies the end date for search. Works only with Use Wordstat 2 option enabled. Must take into account date specification rules |
| Region | All | Search region |
| AntiGate preset | default | You need to pre-configure the  Util::AntiGate scraper - specify your access key and other parameters, and then select the created preset here Util::AntiGate scraper - specify your access key and other parameters, and then select the created preset here |
| AntiGate preset for Login | default | AntiGate preset for login. You need to pre-configure the  Util::AntiGate scraper with parameters, and then select the created preset here Util::AntiGate scraper with parameters, and then select the created preset here |
| Type | All | Device type selection |
| Accounts | Only from "accounts.txt" | Selection of the account usage method: Always auto register - always automatically register accounts "on the fly", requires selecting a configured preset in the SE::Yandex::Register preset parameter. Auto register if no more in "accounts.txt" - first uses existing accounts from accounts.txt, and if they run out - automatic registration "on the fly" is used, for which a configured preset must be selected in the SE::Yandex::Register preset parameter. Only from "accounts.txt" - use only existing accounts from accounts.txt, and if they run out - wait for the specified time (Wait new accounts in "accounts.txt" parameter) for new ones to appear |
| Wait new accounts in "accounts.txt" | 0 | Time to wait for new accounts to appear in accounts.txt |
| Remove bad accounts | Always, except wrong login/password | Automatic deletion of "bad" accounts: Always - always delete. Always, except wrong login/password - always delete, except when Yandex reports an incorrect login/password. This is because Yandex may give such a message when an IP is banned, even for a perfectly working account, so optionally you can keep such accounts for reuse. Never - never delete. Regardless of the selected option, accounts are not deleted in case of proxy/browser errors |
| SE::Yandex::Register preset | default | Selecting a settings preset for  SE::Yandex::Register SE::Yandex::Register |
| Authorization method | HTTP | Authorization method: HTTP - fast, not resource-intensive. Chrome - slow, resource-intensive, theoretically can prolong the life of accounts |
| Chrome headless | ☑ | If the option is enabled, the browser will not be displayed |
| Use sessions | ☑ | Using sessions |
| Do not reset session if authorization passed | ☑ | Do not reset the session on errors if the scraper is already authorized |
| Use Wordstat 2 | ☐ | Using Wordstat 2 |
| Wordstat 2 parse all table data | ☑ | Allows immediate unloading of all 2000 results for a query without passing through pagination |