OpenAI::Completions - OpenAI Completions scraper
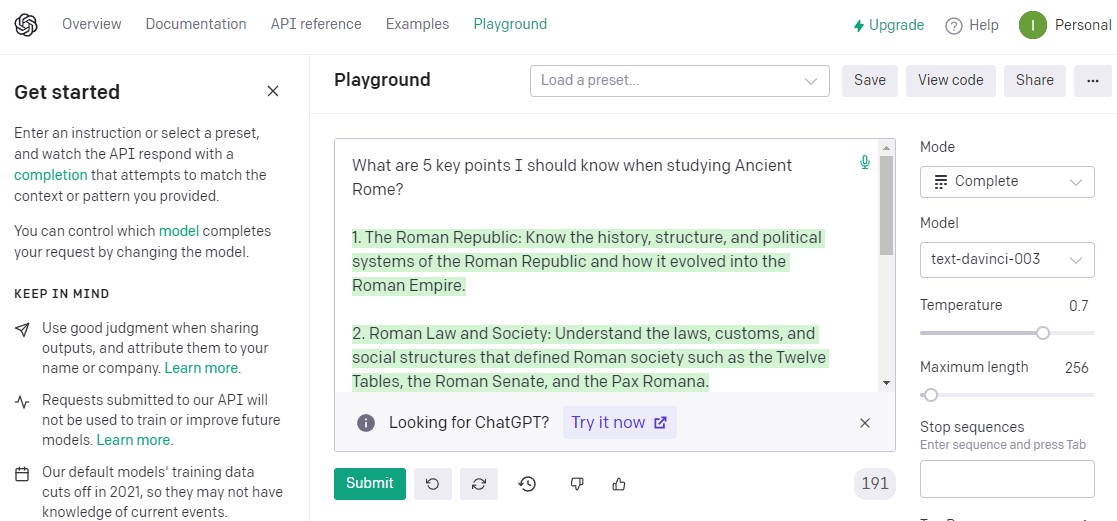
Overview of the scraper
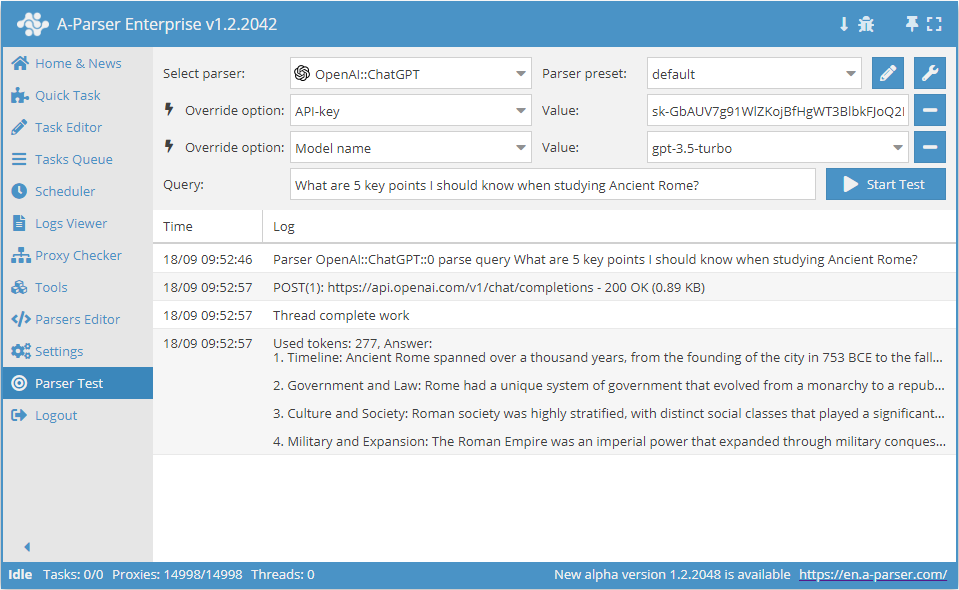
Scraper OpenAI Completions. Scraper for the OpenAI Completions method. It is based on the official API and uses an API key. Similar to the  OpenAI::ChatGPT, scraper, the main difference is the absence of the System prompt content option and other model types for generation.
OpenAI::ChatGPT, scraper, the main difference is the absence of the System prompt content option and other model types for generation.
A-Parser's functionality allows you to save Google scraper settings for future use (presets), ), set a scraping schedule, and much more. You can use automatic query multiplication, substitution of subqueries from files, iteration through alphanumeric combinations and lists to get the maximum possible number of results.
Saving results is possible in the form and structure you need, thanks to the built-in powerful templating engine Template Toolkit which allows you to apply additional logic to the results and output data in various formats, including JSON, SQL and CSV.
Collected data
- Response from OpenAI
- Number of tokens used
Capabilities
- Scrape the response from OpenAI
Use cases
- Generating responses from OpenAI to any questions
Queries
As queries, you need to specify text on a single line, for example:
What are 5 key points I should know when studying Ancient Rome?
Query substitutions
You can use built-in macros to multiply queries.
In the query format, we will specify symbol iteration from a to zzzz, , this method allows maximum rotation of search results and retrieval of many new unique results:
$query {az:a:zzzz}
This macro will create 475254 additional queries for each initial search query, which will total 4 x 475254 = 1901016 search queries. The number is impressive, but it is not a problem at all for A-Parser. At a speed of 2000 requests per minute, such a task will be processed in just 16 hours.
Output results options
A-Parser supports flexible results formatting thanks to the built-in templating engine Template Toolkit, which allows it to output results in an arbitrary form, as well as in a structured format, for example CSV or JSON
Default output
Result format:
Used tokens: $total_tokens, Answer:\n$answer\n
Example result:
Used tokens: 290, Answer:
1. Founding and Early History: Ancient Rome was founded in 753 BCE by twin brothers Romulus and Remus. The city grew to become one of the most powerful and influential empires in world history.
2. Roman Republic: The Roman Republic was established in 509 BCE and lasted until 27 BCE. During this time, Rome developed a complex system of government, with two consuls elected annually, a senate, and assemblies of citizens.
3. Roman Empire: The Roman Empire began in 27 BCE when Augustus became the first Roman emperor. The empire grew to include much of Europe, the Middle East, and North Africa and lasted until the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 CE.
4. Achievements and Contributions: Ancient Rome made significant contributions to architecture, engineering, law, philosophy, art, literature, and language. Roman innovations include the arch, concrete, aqueducts, roads, and the Latin alphabet.
5. Decline and Fall: The Roman Empire faced numerous challenges, including economic instability, political corruption, military defeats, and invasions by barbarian tribes. The Western Roman Empire fell in 476 CE, while the Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire) survived until 1453 CE.
Possible settings
| Parameter | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| API domain | api.openai.com | Ability to change the domain for API requests |
| API key | API key. You can specify several (one per line); for each attempt, a key will be randomly selected from those available and not used within the current request. | |
| Model name | text-davinci-003 | Model type (gpt-3.5-turbo-instruct / babbage-002 / davinci-002) |
| Temperature | 0.7 | Temperature |
| Top P | 1 | Top P |
| Maximum length | 256 | Maximum number of tokens to use |
| Presence penalty | 0 | Presence penalty |
| Frequency penalty | 0 | Frequency penalty |