HTML::EmailExtractor - Scraping Email Addresses from Website Pages
Scraper Overview
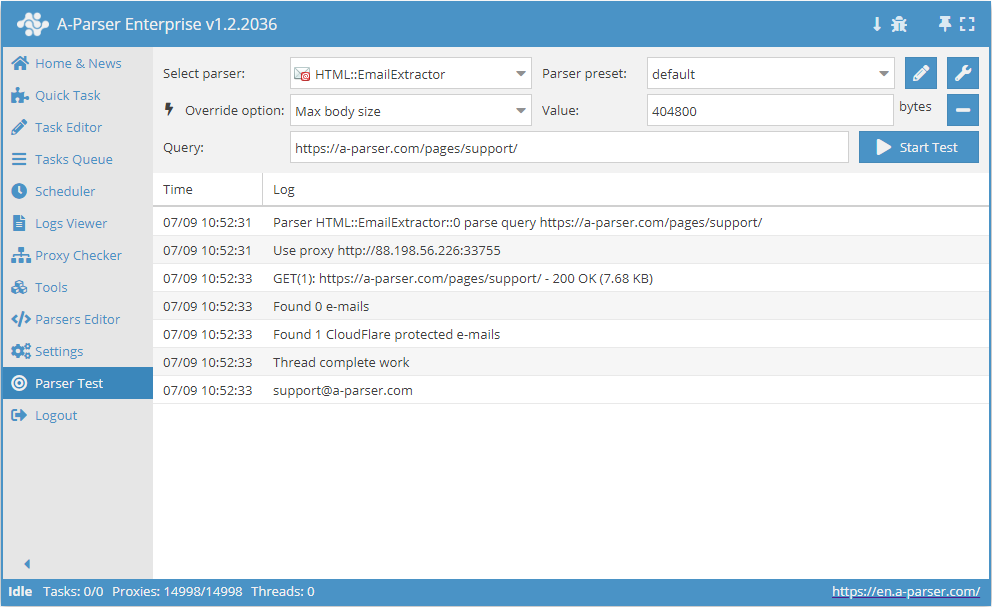
 HTML::EmailExtractor collects email addresses from specified pages. It supports traversing internal site pages up to a specified depth, which allows iteration over all site pages, collecting internal and external links. The Email Scraper has built-in means to bypass CloudFlare protection, and also the option to select Chrome as the engine for scraping emails from pages where data is loaded by scripts. It is capable of speeds up to 250 requests per minute, – which is 15 000 links per hour.
HTML::EmailExtractor collects email addresses from specified pages. It supports traversing internal site pages up to a specified depth, which allows iteration over all site pages, collecting internal and external links. The Email Scraper has built-in means to bypass CloudFlare protection, and also the option to select Chrome as the engine for scraping emails from pages where data is loaded by scripts. It is capable of speeds up to 250 requests per minute, – which is 15 000 links per hour.Scraper Use Cases
Scraping emails from a site by traversing pages up to a specified limit
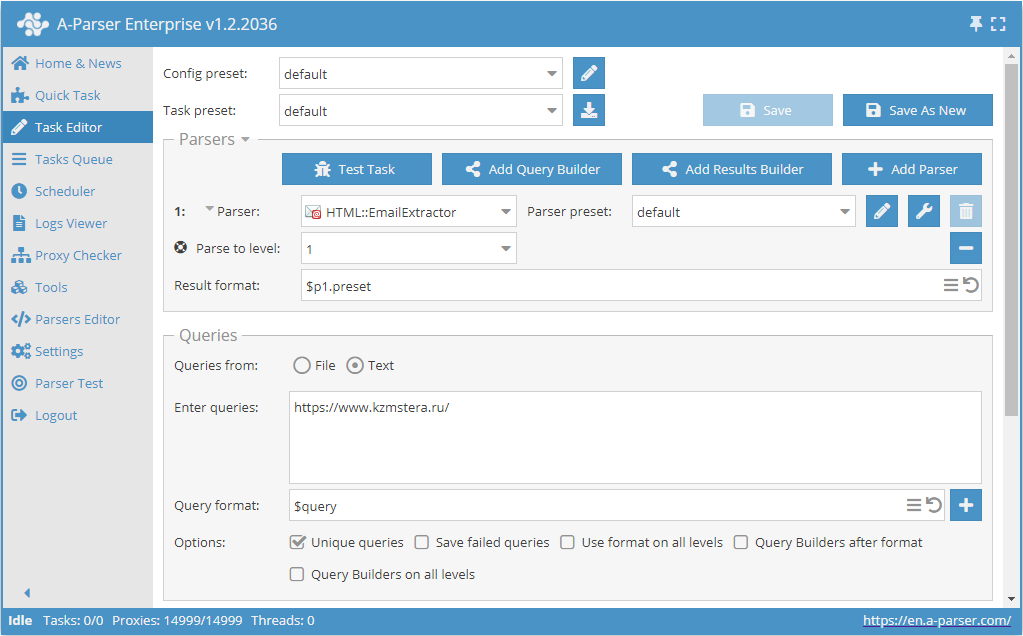
- Add the option Parse to level, and select the required value (limit) from the list.
- In the Queries section, check the
Unique queriesoption. - In the Results section, check the
Unique by stringoption. - As the query, specify the link to the site from which emails need to be scraped.
Download example
How to import an example into A-Parser
eJxtU01z2jAQ/S8aDu0MY5pDL74RJkzTIXGakBPDQYPXREWWVEmGpB7+e98Kx4Ym
N+3u2/f2S62IMuzCg6dAMYh81QqX3iIXJVWy0VGMhZM+kOfwSvxY3i3y/KaWSt+8
Ri830XpAenAr4psjpFsXlTUBMVXCTBwL2pOGZy91A8zVcb0eC+ghM8ytryXrjtxV
1hXRB5/knpYWwUppGtxzWPeyZrlRKSNxNKsS0ZevWXxlBlmWiiuR+qTAbQyqz0b9
4VJEiF6ZLfAwvaIw97aGO1IiYefbe4UrMUq2AE2T8n+dckQefUNjEVDtHAOisg9U
UgdEVCQvMbGiG07eCmumWqfBDLBEf90oXWLs0wpJt13i55DiA8ex7/Bcak/+4FFD
z5Ks6+JuyCrtwm7RuLFoW6taRdhhZhvDu/kG547I9WO7Z1htPfUyHXOnjstyZPgA
hq1N3eC6aONiM5fOjTWV2hZowKuS3pGNWeJ8CzOztdPEfZlGa2wl0ONwIdPQrYGN
ocD/k2dJ4uLwo7U6/Hw6leq8wgV+5wJrTPJctaPcSK2fHxfnETFcFIyXGF3IJ5PD
4ZDt/taBl5r5ZiI4N9LW4qjQ2XHd/7n+Z7af/7y8PWJpv8PDCc4dMhg+jCpgI/zL
/gFm02Dr
Scraping emails from a site database by traversing each site up to a specified depth limit
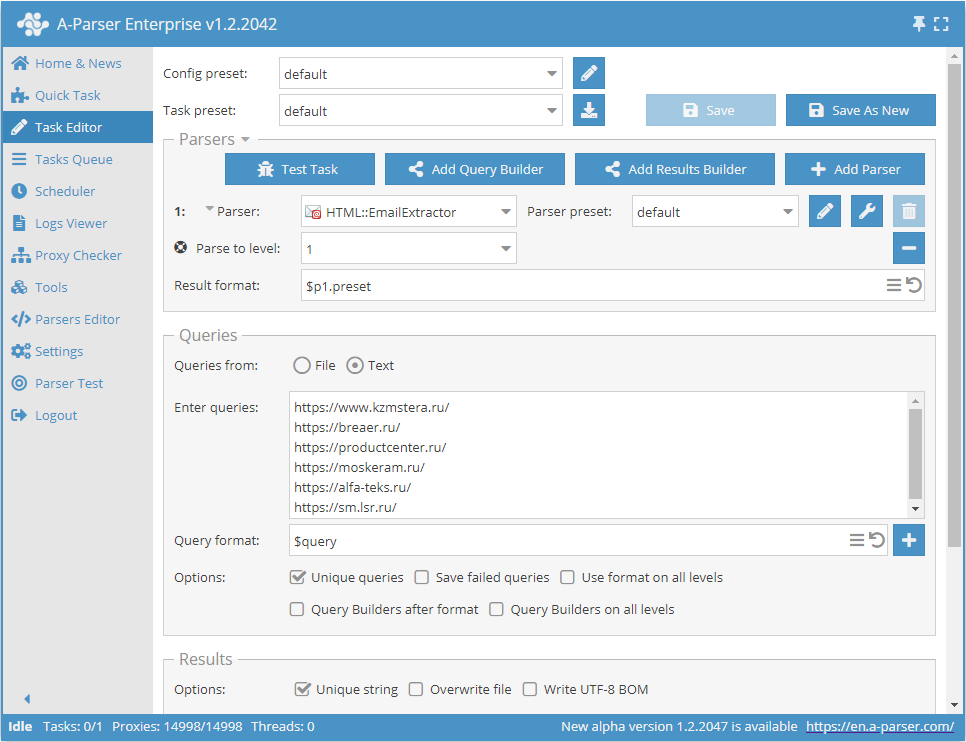
- Add the option Parse to level, and select the required value (limit) from the list.
- In the Queries section, check the
Unique queriesoption. - In the Results section, check the
Unique by stringoption. - As the query, specify the links to the sites from which emails need to be scraped, or in Queries from specify
Fileand upload the query file with the site database.
Download example
How to import an example into A-Parser
eJxtU01z2jAQ/S8aDu0MY5pDL74RJkzTIXGakBPDQYPXREWWVEmGpB7+e98Kx4Ym
N+3u2/f2S62IMuzCg6dAMYh81QqX3iIXJVWy0VGMhZM+kOfwSvxY3i3y/KaWSt+8
Ri830XpAenAr4psjpFsXlTUBMVXCTBwL2pOGZy91A8zVcb0eC+ghM8ytryXrjtxV
1hXRB5/knpYWwUppGtxzWPeyZrlRKSNxNKsS0ZevWXxlBlmWiiuR+qTAbQyqz0b9
4VJEiF6ZLfAwvaIw97aGO1IiYefbe4UrMUq2AE2T8n+dckQefUNjEVDtHAOisg9U
UgdEVCQvMbGiG07eCmumWqfBDLBEf90oXWLs0wpJt13i55DiA8ex7/Bcak/+4FFD
z5Ks6+JuyCrtwm7RuLFoW6taRdhhZhvDu/kG547I9WO7Z1htPfUyHXOnjstyZPgA
hq1N3eC6aONiM5fOjTWV2hZowKuS3pGNWeJ8CzOztdPEfZlGa2wl0ONwIdPQrYGN
ocD/k2dJ4uLwo7U6/Hw6leq8wgV+5wJrTPJctaPcSK2fHxfnETFcFIyXGF3IJ5PD
4ZDt/taBl5r5ZiI4N9LW4qjQ2XHd/7n+Z7af/7y8PWJpv8PDCc4dMhg+jCpgI/zL
/gFm02Dr
Scraping emails by a list of links
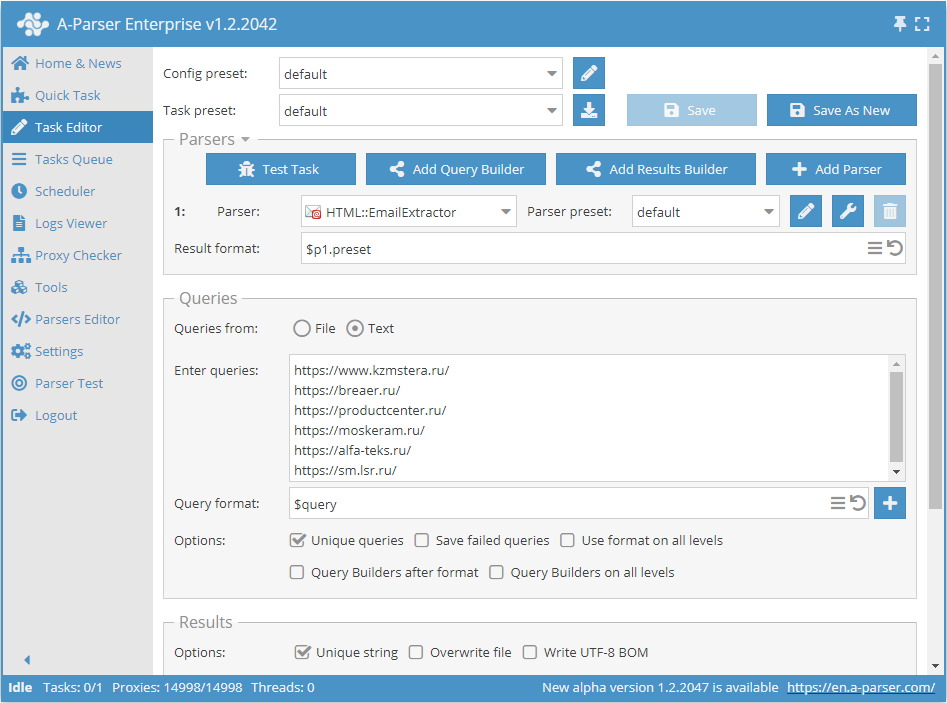
- In the Queries section, check the
Unique queriesoption. - In the Results section, check the
Unique by stringoption. - As the query, specify the links from which emails need to be scraped, or in Queries from specify
Fileand upload the query file with the database of links.
Download example
How to import an example into A-Parser
eJxtU01z0zAQ/S+aHmAmOPTAxbc00wwwaV3a9BRyEPE6COuLXSkpePLfWTmOHZfe
tG/fvv1UI4Kkmh4QCAKJfN0I375FLkqoZNRBTISXSIDJvRafV3fLPL81Uunbl4By
Gxwy5UzebCaCBfhJC4dGJqErf511qr3zSe5h5dhZKQ0DvGDrXhpIUaUMkLxZ1Qq9
e5+Fl6Qgy1IF5azUpwypriHrs1W/Y4qngMrumM8mKqAFOsNwgFYkgX/OFa7FVWsL
lolt/LdTjMgDRpgI4moX3DGUvaOSmtijAqDkERQ+lcR4I5ydab2EPeiB1srfRKVL
nuOs4qAvXeDblOI/jWPf4WWqPeABuYZepbVuirshqnRLt+PGreO2tTIqsE1zF23a
zUcGawDfj+0+0YxD6NN0yl12PhUPtmTmsLWZH6BRG6PNjMGts5XaFdwAqhLOzGhX
fI+FnTvjNaS+bNSat0LwOFzIjLo1JGMo8HXwvE0xuuTgnKavT6dSPSq+wE+pQMOT
vMzaSW6l1s+Py0uPGC6KjZ8heMqn08PhkNV/DaWlZhin3+3Z8wMl4Bjy6Mq4DVuw
4bXLOKpZwoxRqSv5IUBNY5hMpqkVEKnUADvHN8yDPG76P9v/7Obtn5s3R76RX/Rw
oqeBJjJjvBniAxD59fEfH7B6cg==
Collected Data
- Email addresses
- Total number of addresses on the page
- Array with all collected pages (used when the Use Pages option is active)
Capabilities
- Multi-page scraping (page navigation)
- Traverse internal site pages up to a specified depth (the Parse to level) – option allows iteration over all site pages, collecting internal and external links
- Determining follow links for links
- Page traversal limit (Follow links limit option)
- Ability to specify whether subdomains should be considered internal site pages
- Supports gzip/deflate/brotli compression
- Detection and conversion of site encodings to UTF-8
- CloudFlare bypass
- Engine selection (HTTP or Chrome)
- Support for all
 HTML::LinkExtractor
HTML::LinkExtractor
Use Cases
- Scraping email addresses
- Outputting the count of e-mail addresses
Queries
As queries, you must specify links to pages, for example:
https://a-parser.com/pages/support/
Output Result Examples
A-Parser supports flexible result formatting thanks to the built-in templating engine Template Toolkit, which allows it to output results in an arbitrary form, as well as in structured formats like CSV or JSON
Email address count output
Result format:
$mailcount
Example result:
4
Possible Settings
note
| Parameter Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Good status | All | Select which server response is considered successful. If the scraper receives a different server response, the request will be retried with a different proxy |
| Good code RegEx | Ability to specify a regular expression for checking the response code | |
| Ban Proxy Code RegEx | Ability to temporarily ban proxies (Proxy ban time) based on the server response code | |
| Method | GET | Request method |
| POST body | Content to send to the server when using the POST method. Supports variables: $query – request URL, $query.orig – original query, and $pagenum - page number when using the Use Pages option. | |
| Cookies | Ability to specify cookies for the request. | |
| User agent | _Automatically inserts the user-agent of the current Chrome version_ | User-Agent header when requesting pages |
| Additional headers | Ability to specify custom request headers with support for templating features and using variables from the query constructor | |
| Read only headers | ☐ | Read headers only. In some cases, this saves traffic if there is no need to process content |
| Detect charset on content | ☐ | Detect encoding based on page content |
| Emulate browser headers | ☐ | Emulate browser headers |
| Max redirects count | 0 | Maximum number of redirects the scraper will follow |
| Follow common redirects | ☑ | Allows http <-> https and www.domain <-> domain redirects within the same domain, bypassing the Max redirects count limit |
| Max cookies count | 16 | Maximum number of cookies to save |
| Engine | HTTP (Fast, JavaScript Disabled) | Allows selection of HTTP engine (faster, no JavaScript) or Chrome engine (slower, JavaScript enabled) |
| Chrome Headless | ☐ | If enabled, the browser will not be displayed |
| Chrome DevTools | ☑ | Allows using Chromium debugging tools |
| Chrome Log Proxy connections | ☑ | If enabled, information on chrome connections will be output to the log |
| Chrome Wait Until | networkidle2 | Determines when a page is considered loaded. More about values. |
| Use HTTP/2 transport | ☐ | Determines whether to use HTTP/2 instead of HTTP/1.1. For example, Google and Majestic immediately ban if HTTP/1.1 is used. |
| Don't verify TLS certs | ☐ | Disable TLS certificate validation |
| Randomize TLS Fingerprint | ☐ | This option allows bypassing sites banned by TLS fingerprint |
| Bypass CloudFlare | ☑ | Automatic CloudFlare protection bypass |
| Bypass CloudFlare with Chrome(Experimental) | ☐ | CF bypass via Chrome |
| Bypass CloudFlare with Chrome Max Pages | 20 | Max number of pages when bypassing CF via Chrome |
| Subdomains are internal | ☐ | Should subdomains be considered internal links |
| Follow links | Internal only | Which links to follow |
| Follow links limit | 0 | Follow links limit, applied to each unique domain |
| Skip comment blocks | ☐ | Should comment blocks be skipped |
| Search Cloudflare protected e-mails | ☑ | Whether to scrape Cloudflare protected e-mails. |
| Skip non-HTML blocks | ☑ | Do not collect email addresses within tags (script, style, comment, etc.). |
| Skip meta tags | ☐ | Do not collect email addresses in meta tags |
| Search URL encoded e-mails | ☐ | Collect URL encoded emails |